Cortisol Hormone
Cortisol
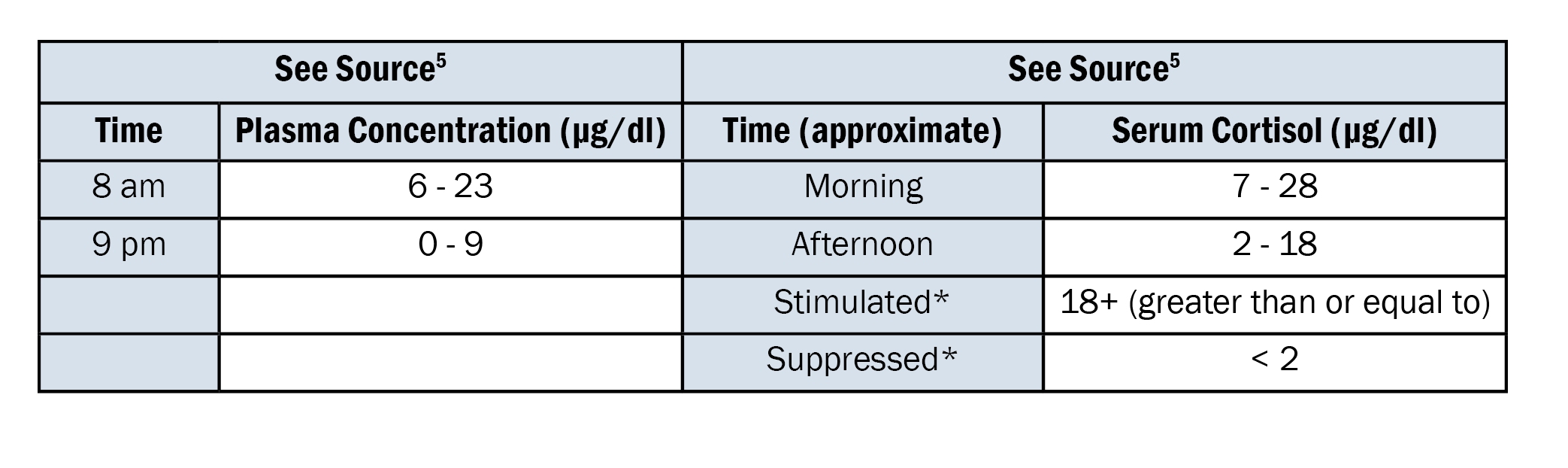
- * Low-dose ACTH stimulation test: before or after (anytime, usually one hour) ACTH 250 μg (one ampule) intravenous injection.
- ** Overnight low-dose dexamethasone suppression test: 8 am serum cortisol after oral dexamethasone 1 mg taken in the late evening (11 pm).
Cortisol is a glucocorticoid steroid secreted by the adrenal gland. It plays a key role in glucose metabolism and stress response. ACTH – or adrenocorticotropic hormone is synthesized by the pituitary gland in response to the hypothalamic corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH). In normal patients, a negative feedback loop in the form of cortisol levels in the blood will inhibit production of CRH and ACTH (this is called the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal [HPA] axis).
Many factors can influence cortisol levels – time of day, sleep schedule of the patient, stress, exogenous glucocorticoids, etc.
Hypercortisolism: characterized by increased serum cortisol levels. This is usually diagnosed via a low-dose dexamethasone suppression test. (Cushing syndrome).
Hypocortisolism: characterized by decreased serum cortisol levels. One screening test is the ACTH stimulation test which involves measuring serum cortisol (and ACTH) immediately before and ~1 hour after an intravenous injection of 250 μg of cosyntropin.
Reference: